Flowers
adapted from Woody Plants of the Blue Ridge by Ron Lance. Used by permission.
To see photographic examples of a term, click the camera next to it in the list of botanical terms.
Gymnosperms produce egg cells in conelike structures without ovaries, and are frequently referred to as non-flowering plants.
Angiosperms (flowering plants) have true flowers, with pistils and stamens.
The pistil is “female”: contains an ovary and ovule(s).
Stamens are “male”: produce pollen.
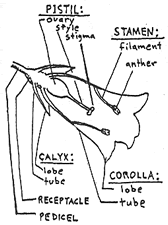
Non-reproductive flower structures in flowers are the corolla (petals) and the calyx (sepals). Sometimes one or both of these are lacking, and sometimes they are difficult to distinguish.
The receptacle is the basal area of a flower which bears the parts;
the pedicel is the flower stalk.
Bracts or bractlets are leaf-like or petal-like appendages, sometimes attached to the base of a pedicel or in an inflorescence in many plants.
Corolla lobes and tubes maybe present, as same with calyx. Petals or sepals may be lobed or fringed.
Pistils may be simple (one unit), or compound (several fused or separate units per flower).
Monoecious plants ... the pistillate and staminate flowers are separate but on the same individual.
Dioecious plants have either pistillate or staminate flowers only — thus individual plants are of one sex.
Polygamous plants have unisexual and bisexual flowers.
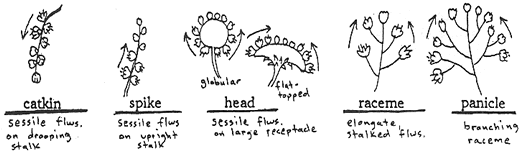
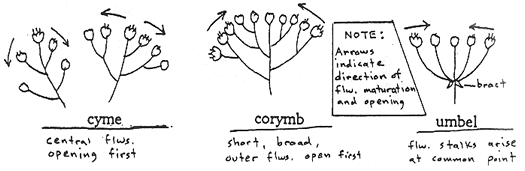
Inflorescences: Flowers occurring in groups or clusters are arranged in some particular form called an inflorescence. Bracts are often seen on flower stalks within, or on basal areas of inflorescences. Some common inflorescence types of woody plants are: